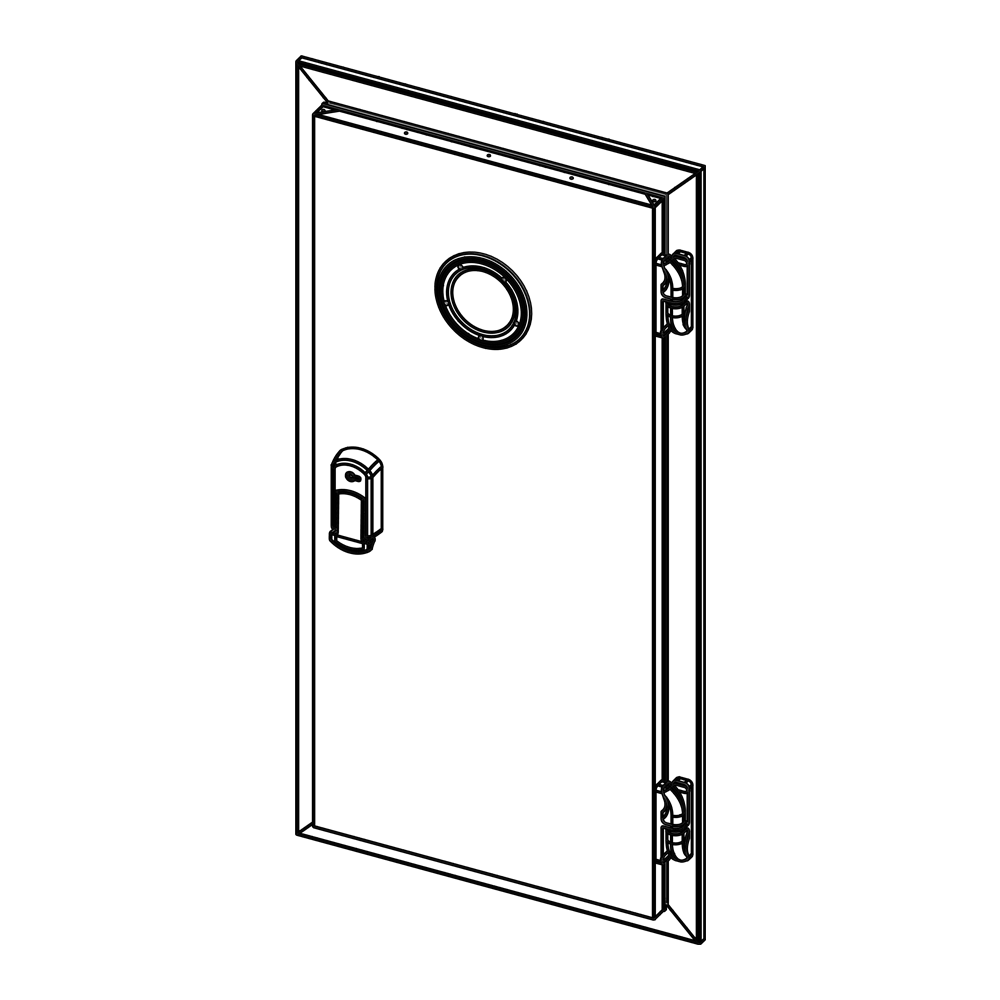
Cold Room Observation Glass (Porthole)
The Function of the Porthole in Cold Room Systems
In cold room systems, the porthole, referred to as an observation window, is a specially insulated glass system that allows viewing the interior from the outside. Thanks to these windows, the condition of products, shelves, equipment, or personnel inside can be checked without opening the room’s door. Portholes provide ease of monitoring in areas where temperature-sensitive products such as food, pharmaceuticals, chemical substances, or laboratory samples are stored, while also helping to maintain the cold chain.
Modern cold room systems today are highly advanced in terms of energy efficiency and temperature control. The use of portholes in these systems minimizes heat loss while allowing operators to visually monitor operations. Since activities inside the room can be controlled from the outside without heat loss, savings in energy efficiency are achieved.
Structural Features of the Porthole
Portholes are typically manufactured as double or triple-glazed units. A gap is left between these glass layers, filled with argon gas, dry air, or a vacuum. This ensures both thermal insulation and prevents fogging on the glass surfaces. Tempered or laminated glass is commonly used in their production. These glass types are resistant to both thermal and mechanical impacts and are designed to shatter safely without fragmenting in case of breakage.
Some porthole models incorporate heated glass technology. Transparent resistive layers integrated into the inner surface of the glass prevent fogging and freezing at low temperatures. This system offers significant advantages, particularly in deep-freezer applications below -18°C.
Materials Used and Technical Details
Porthole frames are important for both aesthetics and durability. Stainless steel, anodized aluminum, PVC, or composite materials are commonly used in frame production. These materials provide long-lasting and durable solutions for the cold room environment. Additionally, sealing gaskets, silicone fillers, and insulation strips used during installation play a critical role in preventing thermal bridges between the glass and the panel.
The gap between the glass layers is sealed using a hermetic sealing method. During this process, butyl or polysulfide-based sealants are applied to the glass edges. This prevents moisture ingress and ensures that fogging on the glass surfaces is prevented for an extended period.
Anti-Fog and Visual Clarity
One of the most important functions of cold room glass is anti-fog. Fogging on the glass surface reduces visibility and negates the glass’s functionality. For this reason, most portholes feature anti-fog coating. This technology, applied as a special film or chemical layer on the inner surface of the glass, prevents fog formation.
Alternatively, heated glass systems can be used. These systems contain thin conductive layers that generate heat using electrical energy. By maintaining a constant glass surface temperature, condensation is prevented. This technology becomes indispensable, especially in systems operating continuously at -25°C or below.
Contribution to Energy Efficiency
Portholes are not only used for observation but are also a significant component for energy efficiency. Frequent opening of cold room doors disrupts the internal temperature balance, causing cooling systems to consume more energy. With a porthole, operators can check the interior without opening the door, reducing energy consumption while enhancing product quality.
Additionally, thanks to their double-glazed and thermal insulation design, portholes block heat from the external environment. This allows the cold room’s internal temperature to remain more stable. This feature is particularly important in high-temperature-sensitivity areas such as food storage, medical product rooms, and laboratories.
Applications
Portholes are widely used not only in the food industry but also in various other fields. Pharmaceutical warehouses, blood banks, biological product storage rooms, laboratories, logistics centers, and chemical substance storage facilities are among these. In these areas, continuous monitoring of products is necessary, but frequent door openings pose risks to product quality and safety. Thus, porthole usage stands out as a critical solution.
In some cases, UV-protective coatings are added to the glass surfaces of portholes. These coatings prevent UV rays from sunlight or artificial lighting from entering the cold room. This is particularly important for protecting products sensitive to UV radiation.
Installation and Assembly Details
Key considerations during the installation of portholes include wall thickness, panel type, installation opening, and frame compatibility. Portholes are typically mounted on sandwich panel walls and must be sized according to the panel thickness. Incorrect measurements or installation can reduce the glass’s insulation performance or cause issues like fogging and leaks.
During installation, the frame must be properly seated, and no air gaps should remain when placing the glass. Installation screws, insulation tape, and sealing materials must be used correctly. Additionally, some porthole models feature removable frame systems to facilitate cleaning and maintenance.
Size and Customization Options
Portholes can be produced in various sizes and shapes tailored to the project. While standard sizes like 400x600 mm or 500x800 mm are commonly used, square, rectangular, or circular forms can be manufactured based on needs. Additionally, options such as glass thickness, heating features, UV protection, or colored glass can be added based on customer requirements. These customization options vary depending on the cold room’s purpose and layout.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity of portholes. Glass surfaces should be cleaned with appropriate chemicals, and microfiber cloths should be used to avoid scratches. If fogging or signs of leakage are observed on the glass surface, the gaskets should be checked. In heated glass systems, regular testing of the heating circuits is crucial for safe operation.
Visual Monitoring and Safety Applications
In cold room systems, porthole usage is important not only for monitoring but also for safety. In areas storing pharmaceuticals, biological materials, or valuable food products, the ability to observe activities from the outside enhances personnel safety. Some systems allow camera integration on porthole glass, enabling real-time monitoring or recording of internal operations from a central location.
Additionally, in emergency scenarios, portholes serve a vital function by allowing trapped personnel to be noticed. In terms of confined space worker safety, the glass enables visual contact with the outside, facilitating immediate intervention in case of issues.
Portholes in Reducing Thermal Bridge Effects
Thermal bridges are points in building systems that negatively affect energy efficiency. In cold room walls, such bridges often occur at glass or metal junctions. However, modern porthole systems use thermal barrier frame systems to minimize this effect. These frames reduce conductivity between the inner and outer surfaces, minimizing heat transfer.
Additionally, low-emissivity (low-E) coatings used between glass layers provide extra resistance to heat transfer. These coatings reduce energy loss from the glass, which is particularly significant in facilities aiming for green building certifications like LEED.
Special Glass Technologies and Smart Portholes
In next-generation porthole systems, smart glass technologies are being introduced. These glasses can switch from transparent to opaque using electrochromic glass technology when an electric current is applied. This allows operators to toggle between making the interior visible or private. This technology can be beneficial for data privacy in laboratories, pharmaceutical production, or R&D rooms.
Another innovation is solar-controlled glass systems. These glasses automatically adjust their transparency level based on incoming light intensity, preventing harmful UV effects while maintaining internal temperature balance.
Portholes Standards and Certification
The production and use of cold room glass are regulated by certain international standards. The most commonly used standards include:
- EN 1279 (Performance of insulated glass units)
- ISO 12543 (Durability of laminated glass)
- EN 12150 (Tempered glass standard)
- HACCP compliance (Glass surface cleanliness for food safety)
Additionally, CE certification, RoHS, and REACH compliance of the products offered by manufacturers are considered quality indicators. Portholes used in medical applications must pass biocompatibility and chemical resistance tests.
Colored and Patterned Glass Options
In projects where aesthetics are a priority, glass can be produced in different color tones. Especially in cold rooms open to customer areas, gray, blue, or bronze tones can be applied to the glass. These tones help block sunlight and enhance architectural harmony.
In some projects, decorative patterns are applied to glass surfaces using techniques like screen printing, sandblasting, or film coating. These techniques make portholes not only functional but also an integral part of the project’s architectural design.