Hygienic Profile
Table of Contents
- What is a Hygienic Profile?
- Key Features of Hygienic Profiles
- Usage Areas of Hygienic Profiles
- Advantages of Hygienic Profiles
- Tips for Choosing the Right Hygienic Profile
- Maintenance and Cleaning of Hygienic Profiles
- Technological Innovations in Hygienic Profiles
What is a Hygienic Profile?
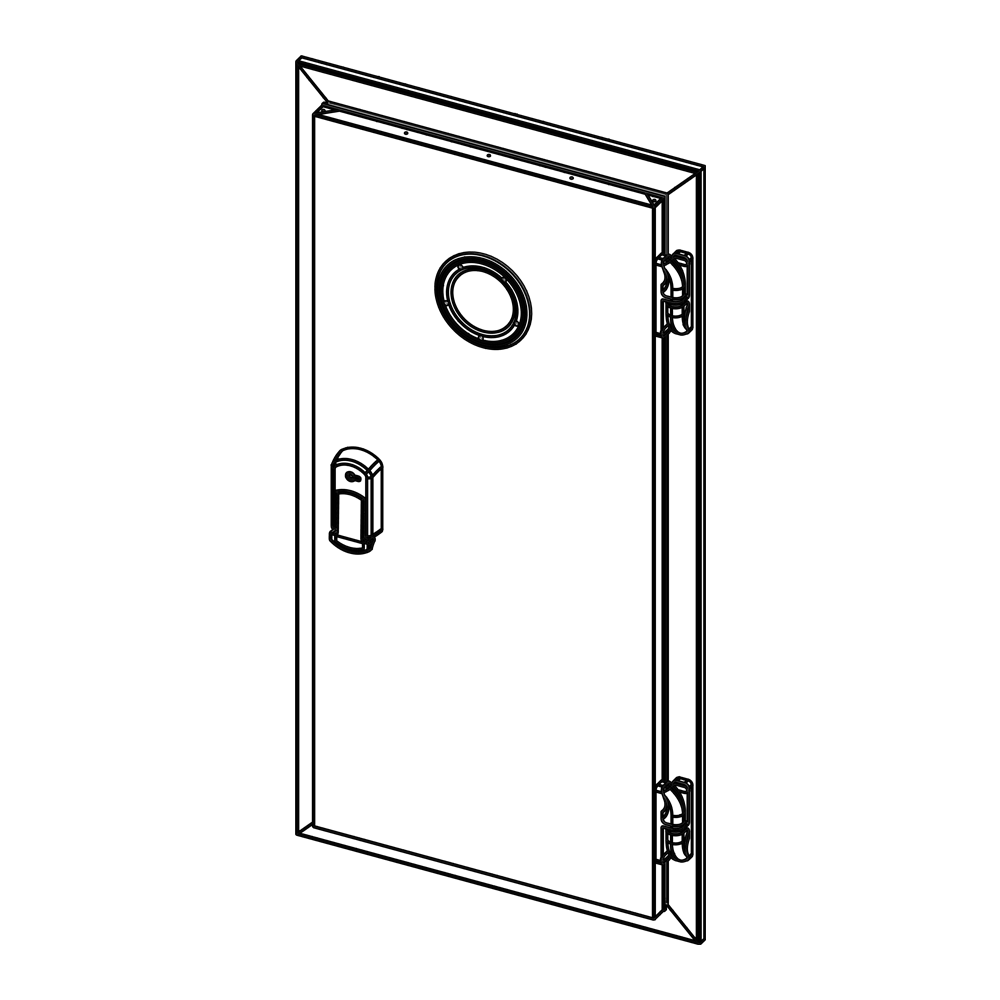
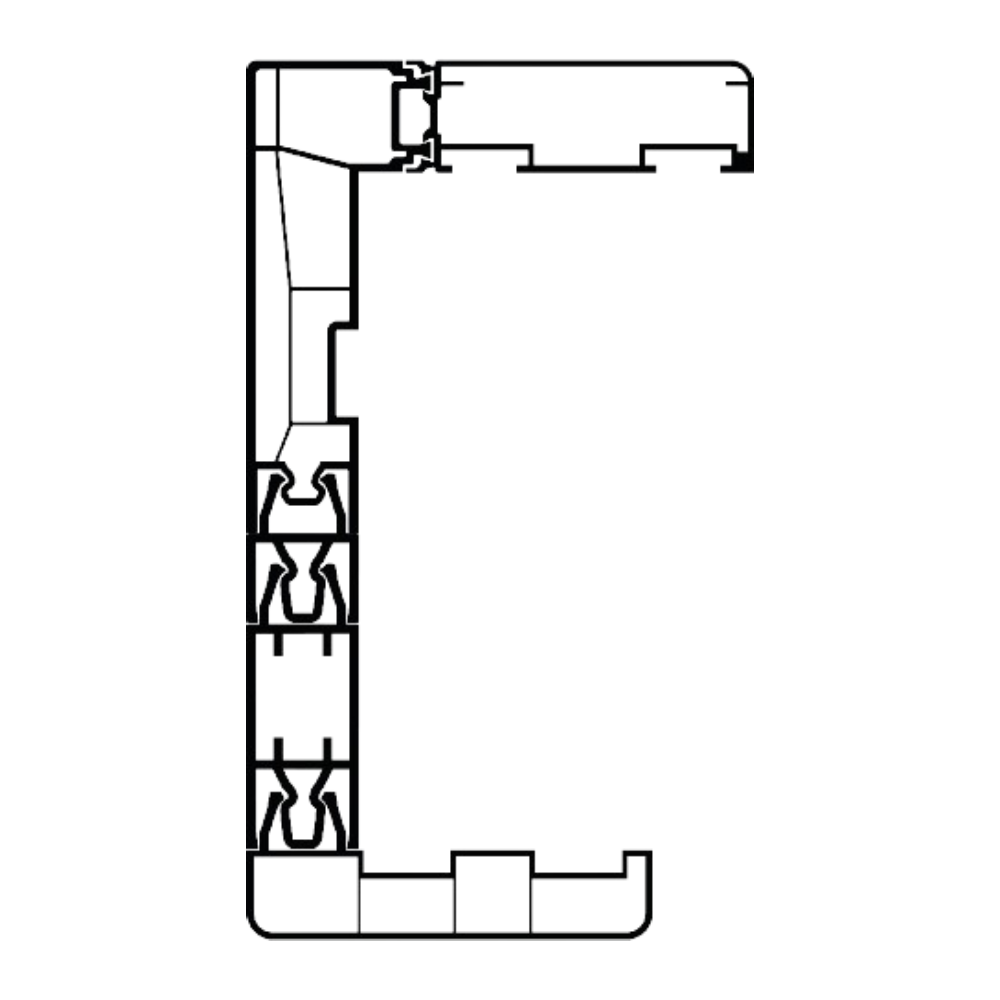
A hygienic profile is a specially designed construction material used in industries where cleaning and safety are paramount. Typically made from stainless steel, aluminum, or high-quality polymers, these profiles are engineered to prevent bacterial growth, provide surfaces that facilitate easy cleaning, and resist corrosion. They are widely used in sectors such as food production, pharmaceuticals, healthcare, and chemical industries. The hygienic profile combines aesthetics and functionality, enabling facilities to comply with stringent hygiene standards. Hygienic profiles minimize dirt accumulation with their smooth surfaces and rounded edges. Sealed connection points prevent liquid or particle leakage, ensuring compliance with critical standards like food safety. For instance, hygienic profiles used in food processing facilities are manufactured to meet international regulations, enhancing product safety. Their modular structure allows for quick assembly and disassembly, supporting operational flexibility for businesses. In modern industries, a hygienic profileis not just a building material but a key component that ensures safety and efficiency.
Key Features of Hygienic Profiles
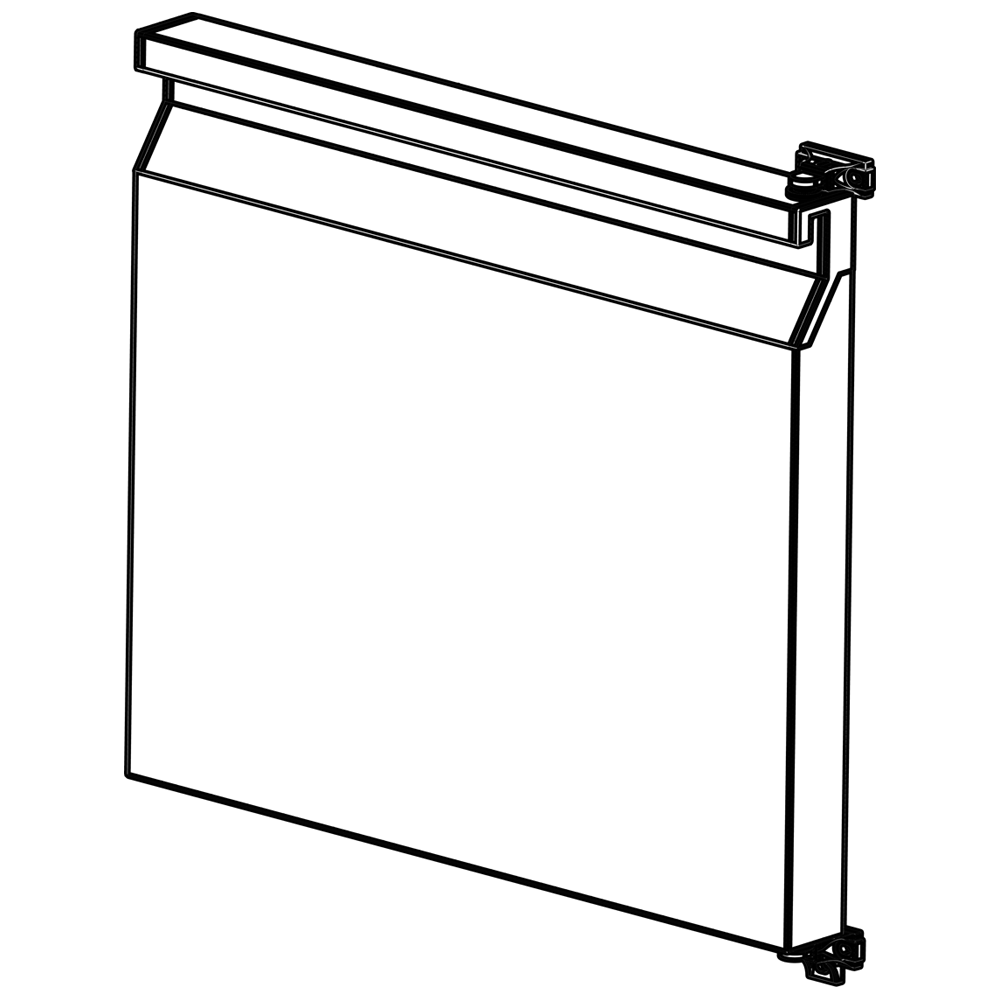
Hygienic profiles stand out from other construction materials due to their unique features. Primarily, they are made from corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel. Stainless steel delivers long-lasting performance in humid or chemically exposed environments. Some hygienic profiles are equipped with antimicrobial coatings, which prevent bacteria, mold, and other microorganisms from adhering to surfaces, thereby elevating hygiene levels. Smooth, non-porous surfaces are among the most significant features of hygienic profiles. These surfaces prevent dirt buildup and simplify cleaning processes. Cleaning with water, detergents, or disinfectants reduces the risk of cross-contamination. Rounded corners and sealed joints eliminate hard-to-reach areas during cleaning. Modular designs make hygienic profileseasy to install and reconfigure. Additionally, some profiles offer resistance to heat and UV rays, ensuring adaptability to various industrial conditions.
Usage Areas of Hygienic Profiles
Hygienic profiles play a vital role across diverse industries. The food and beverage sector is one of the primary areas of use. In dairy plants, meat processing lines, ready-to-eat food production units, and beverage bottling facilities, hygienic profiles are employed in both equipment and facility infrastructure. These profiles ensure compliance with food safety standards, maintaining product quality and simplifying audits. The pharmaceutical industry is another critical area for hygienic profiles. In pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, these profiles are used in wall cladding, floor connections, and equipment frames to create sterile environments. In healthcare, hospitals, operating rooms, and cleanrooms rely on hygienic profiles for infection control. In the chemical industry, stainless steel profiles resistant to chemicals enhance facility safety. Emerging sectors like cosmetics production and biotechnology are also increasingly adopting hygienic profiles.
Advantages of Hygienic Profiles
Hygienic profiles offer both operational and economic benefits to businesses. They ensure facilities meet hygiene standards, providing a competitive edge during inspections, particularly for operations adhering to food safety regulations. Profiles made from stainless steel or high-quality polymers are durable, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and offering long-term cost savings. The balance between aesthetics and functionality is another advantage of hygienic profiles. Their modern, clean appearance helps facilities project a professional image. Easy assembly and disassembly features allow businesses to reconfigure facilities swiftly. Hygienic profilesmade from eco-friendly materials support sustainability goals. Recyclable materials make them an ideal choice for environmentally conscious businesses. Additionally, energy-efficient designs help lower operational costs.
Tips for Choosing the Right Hygienic Profile
Selecting a hygienic profile requires careful consideration of the facility’s needs and industry requirements. The material type is the first factor to determine. Stainless steel offers high corrosion resistance, while polymer-based profiles are lighter and more cost-effective. Environmental conditions, such as high humidity or exposure to acidic substances, dictate material choice, with stainless steel hygienic profiles being preferable for such settings. Design features are critical for cleaning ease. Rounded corners, sealed joints, and smooth surfaces maintain hygiene standards. Modular designs provide flexibility for future modifications. Compliance with certifications, such as FDA or EHEDG for food safety, should be verified. The manufacturer’s technical support and warranty terms are also important for long-term reliability.
Maintenance and Cleaning of Hygienic Profiles
Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential for the longevity of hygienic profiles. Cleaning should use detergents suited to the profile’s material. Stainless steel profiles require non-abrasive cleaners and should be dried with a soft cloth. Polymer-based profiles should follow manufacturer-recommended products. Soft sponges or cloths prevent surface scratches during cleaning. The frequency of cleaning depends on the facility’s usage intensity. Food production facilities may require daily cleaning protocols, while healthcare settings may need sterilization. Joints and corners should be regularly checked to prevent dirt buildup. Periodic maintenance helps identify and repair surface damage on hygienic profiles. For instance, scratches on stainless steelsurfaces can be polished, preserving both hygiene and aesthetics.
Technological Innovations in Hygienic Profiles
Hygienic profile technology continues to evolve to meet industry demands. Antimicrobial coatings and nanotechnology-based surfaces have enhanced the effectiveness of hygienic profiles. These innovations make it nearly impossible for microorganisms to adhere, reducing cleaning frequency. Hygienic profiles integrated with smart sensors enable real-time hygiene monitoring. 3D printing technology has revolutionized the customization of hygienic profiles. It allows rapid production of profiles tailored to specific facility needs. For example, hygienic profiles produced via 3D printing offer perfect fit and sealing in complex facility layouts. Eco-friendly production processes and recyclable materials prioritize sustainability in the hygienic profile industry. These advancements boost business efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.