Cold Room Sliding Doors
Definition and Function of Cold Room Sliding Doors
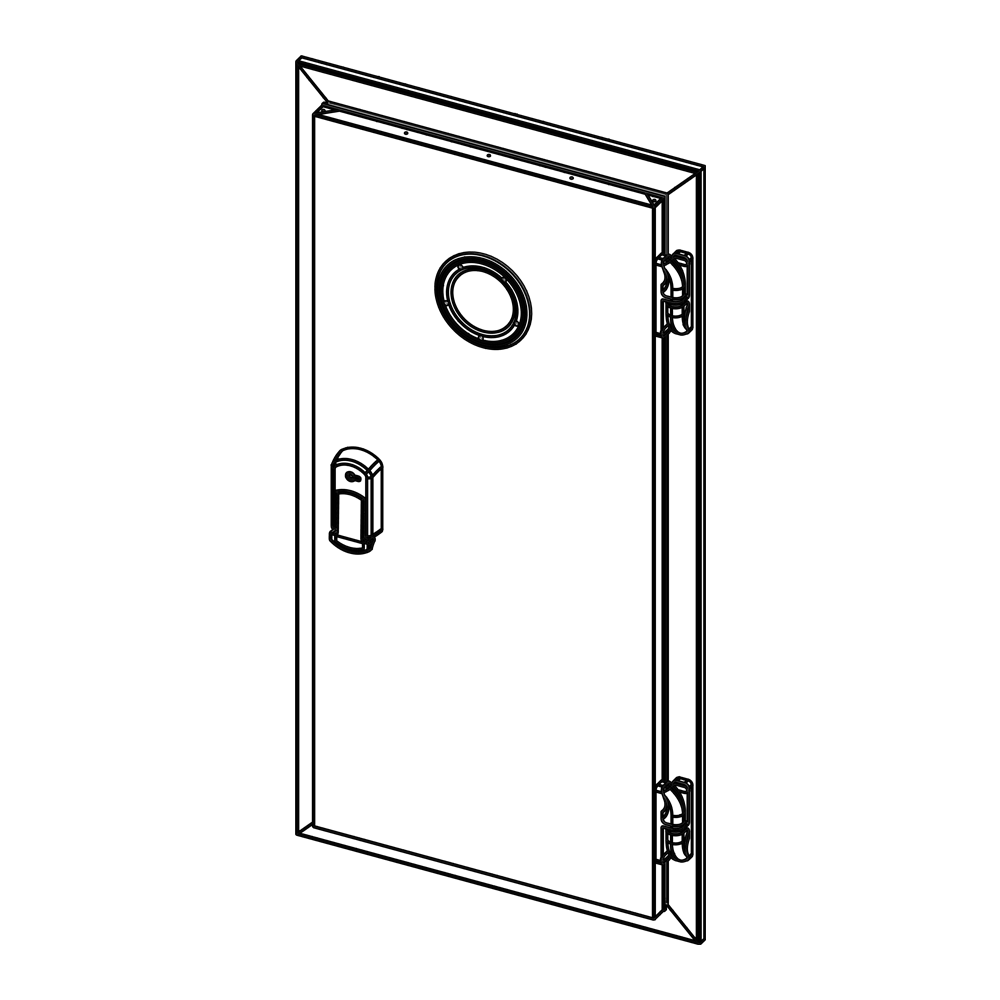
Cold room sliding doors are highly insulated door systems used in industrial refrigeration systems, cold storage facilities, and areas requiring precise temperature control. These doors are installed at the entry-exit points or internal partitions of cold rooms, minimizing energy loss, maintaining stable internal temperatures, and supporting hygiene standards. Thanks to their sliding mechanisms, the doors open and close horizontally, saving space in areas with wide entrances and allowing quick passage. Widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, logistics, and retail sectors, these doors are designed to protect product safety and reduce operating costs.
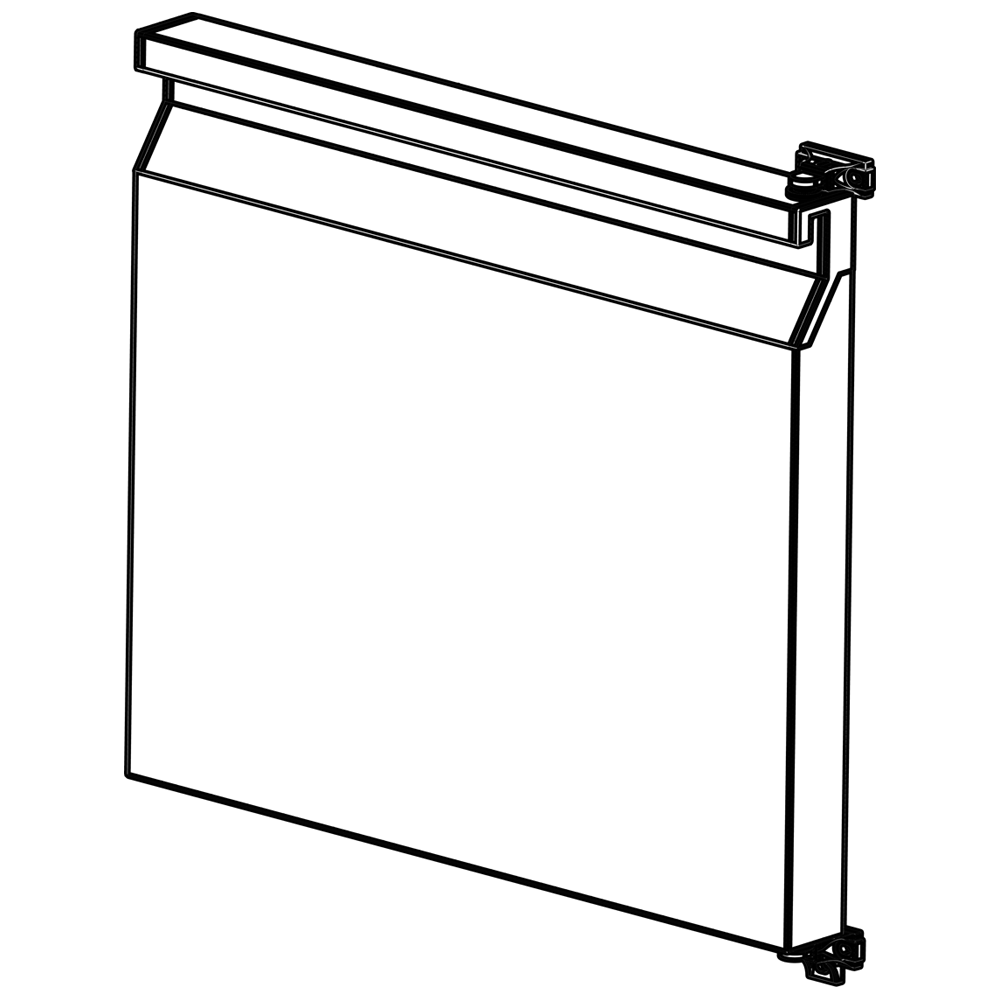
Sliding doors typically consist of polyurethane foam-filled panels, providing high insulation performance. The door panels are coated with durable materials such as stainless steel, galvanized steel, or aluminum. Their thickness varies from 60 mm to 120 mm, depending on the cold room’s temperature requirements. For example, 60-80 mm thickness is sufficient for standard cold rooms operating between 0°C and 5°C, while 100-120 mm thick doors are preferred for blast freezing rooms reaching -40°C. These doors are equipped with special gaskets and insulation profiles to enhance airtightness, maximizing energy efficiency and hygiene.
Structural Features and Technical Advantages
Cold room sliding doors are specifically designed to meet the needs of high-performance refrigeration systems. The door panels are filled with high-density polyurethane foam, providing excellent thermal insulation. Polyurethane foam, with its low thermal conductivity, can reduce energy loss by up to 40%. The door surfaces are typically made of stainless steel or food-safe painted galvanized steel, which are resistant to corrosion in humid and cold environments.
The rail systems of sliding doors are made of aluminum or stainless steel and function smoothly even at low temperatures. The rails ensure easy sliding of the door and resist deformation under heavy loads. Some models feature automatic sliding systems or sensor-based opening-closing mechanisms to enhance operational efficiency. Door gaskets, typically made of silicone or EPDM materials, provide airtight sealing. These gaskets remain flexible down to -50°C and are resistant to wear over long-term use.
The doors also offer superior safety features. For instance, emergency locks or internally operable safety handles eliminate the risk of personnel being trapped. Transparent observation windows increase visibility on both sides of the door, ensuring safety during forklift or pedestrian passages. Additionally, some doors are equipped with antimicrobial coatings, supporting hygiene standards in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Applications and Sectoral Uses
Cold room sliding doors are used in various sectors where energy efficiency and hygiene are critical. In the food industry, these doors maintain product quality by controlling temperature in cold rooms storing meat, fish, dairy products, fruits, vegetables, and frozen foods. For example, in a meat processing facility, sliding doors in large warehouses with frequent entry-exit operations provide both energy savings and quick access.
In the pharmaceutical industry, sliding doors create a hygienic barrier in cold rooms storing vaccines, blood products, and other sensitive medical materials. They prevent the entry of dust, dirt, and microorganisms, ensuring compliance with strict regulations. In cold chain logistics, sliding doors offer a fast and reliable solution for large-scale warehouses where products are kept at stable temperatures during transport and temporary storage.
In commercial kitchens, restaurants, hotels, and supermarkets, sliding doors save space and facilitate passage in high-traffic areas. For instance, in a supermarket’s back storage, sliding doors in cold rooms with wide entrances enhance operational efficiency. In laboratories and clean rooms with high hygiene requirements, the smooth surfaces and antimicrobial coatings of these doors provide significant advantages.
Advantages and Operational Contributions
Cold room sliding doors offer multifaceted benefits to businesses:
- High Energy Efficiency: Polyurethane foam-filled panels and airtight gaskets reduce energy loss by 30-40%, lowering electricity costs, especially in large-scale cold rooms.
- Fast and Safe Access: The sliding mechanism allows quick opening and closing in wide entrances, facilitating personnel and vehicle passage. Transparent windows reduce the risk of collisions.
- Hygiene and Cleanliness: Smooth surfaces and antimicrobial coatings ensure easy cleaning and prevent bacterial growth, guaranteeing compliance with sanitation standards in the food and pharmaceutical sectors.
- Durability: Stainless steel or galvanized coated panels ensure long-term use in humid and cold environments. Rail systems are designed to withstand heavy usage.
- Flexibility and Customization: Doors can be customized in various sizes, thicknesses, and colors to suit any cold room design.
Production Process and Material Quality
The production of cold room sliding doors requires high engineering standards and quality control processes. Production begins by considering the cold room’s dimensions, temperature range, and intended use. Door panels are manufactured with polyurethane foam injection, ensuring high insulation performance. Surface coatings, typically made of stainless steel, galvanized steel, or aluminum, undergo special treatments to resist corrosion.
Rail systems are designed based on the door’s weight and usage frequency. Aluminum or stainless steel rails operate smoothly at low temperatures and are durable. Gaskets, made of silicone or EPDM materials, undergo airtightness tests. During production, the doors’ insulation, durability, and safety features are tested for compliance with international standards (e.g., EN or ISO). Some doors are equipped with antimicrobial coatings or UV-resistant surfaces to meet specific industry needs.
Material selection is customized based on the intended use. In the food industry, hygienic stainless steel surfaces are preferred, while more cost-effective galvanized steel is used in logistics warehouses. Transparent windows, typically made of polycarbonate or acrylic, offer high impact resistance.
Door Types and Models
Cold room sliding doors are produced in various models to meet different needs:
- Standard Sliding Doors: 60-80 mm thick, suitable for cold rooms operating between 0°C and 5°C.
- Blast Freezer Doors: 100-120 mm thick, designed for extreme cold rooms reaching -40°C.
- Automatic Sliding Doors: Equipped with sensor-based or remote-controlled systems, used in large warehouses.
- Custom-Sized Doors: Produced specifically for large or small entrances.
- Hygienic Doors: Equipped with antimicrobial coated panels, tailored for the food and pharmaceutical industries.
This variety provides solutions tailored to different industries, expanding the doors’ application range.
Installation and Maintenance Guide
Proper installation of cold room sliding doors is critical to maintaining their performance over time. Installation must be carried out by expert teams, ensuring perfect alignment with the entrance dimensions. Rail systems should be aligned to ensure smooth sliding, and gasket airtightness must be tested during installation.
For maintenance, door surfaces should be regularly cleaned with hygienic cleaners. In the food industry, chemically resistant surfaces are preferred. Rail systems should be periodically checked and lubricated to prevent dust and dirt accumulation. Gasket wear should be regularly inspected and replaced as needed. These measures ensure the doors remain both functional and hygienic.
Production and Market Dynamics in Turkey
Turkey has a strong infrastructure for producing cold room sliding doors. Local companies produce high-quality and cost-effective doors, competing in both domestic and international markets. For example, some Turkish manufacturers produce hygienic doors for the food and pharmaceutical industries, while others offer durable and automatic doors for the logistics sector. Companies provide detailed technical support and customization options to meet customer needs. Turkey holds a significant position in this field, exporting to Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
Technological Innovations and Future Perspectives
Cold room sliding doors are continually evolving with technological advancements. Smart doors equipped with sensors can monitor temperature and humidity levels, optimizing energy efficiency. Eco-friendly materials and recyclable panels contribute to sustainability goals. Automatic door systems facilitate quick passage in large warehouses, enhancing operational efficiency. In the future, thinner yet highly insulated panels and advanced sensor technologies could further increase energy savings, providing significant advantages for businesses aiming to reduce costs.